関連ワード:
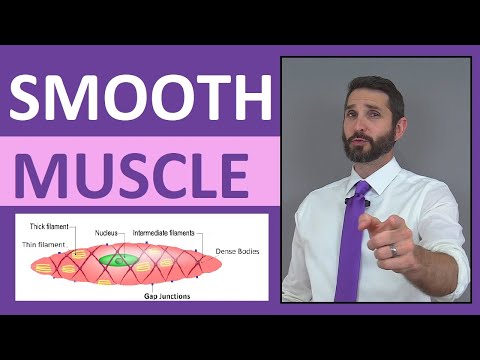
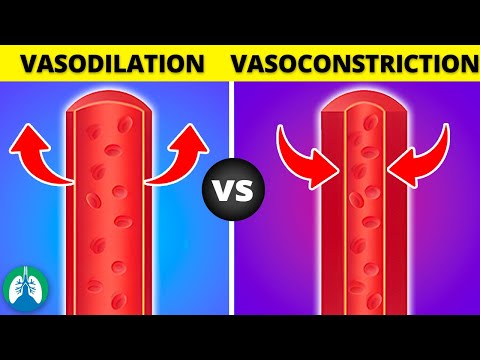
smooth muscle in blood vessels smooth muscle in blood vessels function smooth muscle in blood vessel walls vascular smooth muscle in blood vessels helps to smooth muscle cells in blood vessels smooth muscle contraction in blood vessels smooth muscle tissue in blood vessels smooth muscle in peripheral blood vessels vascular smooth muscle in blood vessels helps to quizlet smooth muscle found in blood vessels