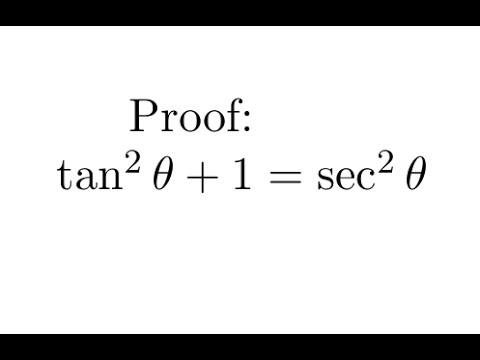関連ワード:
tan 2 theta is equal to 1 tan 2 theta into tan theta is equal to 1 tan square theta sec 2 theta is equal to 1 1 tan 2 theta is equal to dash 1 tan 2 θ is equal to 1 tangent 2 theta is equal to √ 1 tan 2 theta is equal to root 1 tan 2 theta is equal to √ 1 tan 2 theta is equal to mcq tan theta is equal to 1 upon 2