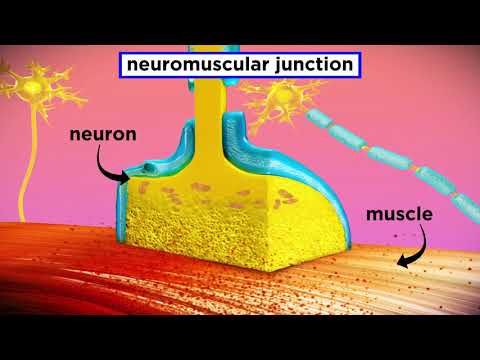
関連ワード:
why do skeletal muscle fibers look striated why do skeletal muscle fibers appear striated why do skeletal muscle fibers appear striated when viewed through a light microscope why does skeletal muscle fibers appear striated why do skeletal muscle cells appear striated why do skeletal muscle cells look striated striated when looking at them under a microscope explain why skeletal muscle fibers look striated why does skeletal muscle look striated what causes the striated appearance of skeletal muscle why are muscle fibers striated